Action :
tom.beanrsc (Category :
tom, Name :
beanrsc, By :
kikonf)
Complete Name :
tom.beanrsc.by.kikonf
Version :
4.0 License :
Modified BSD License
Purpose of the tom category :
Easy to customize. This category use in background the Kikonf Repoz tools to create and configure
Apache Tomcat ®
root installs and
Catalina bases at any level (
server.xml,
hosts or
defaults).
You can use it to manage the whole
Tomcat ® Architecture.
Purpose of this beanrsc plugin : This Action configures a Tomcat Bean Factory Resource.
The following shows in what part of a typical Architecture is likely to be found, the Resource configured by Action : tom.beanrsc
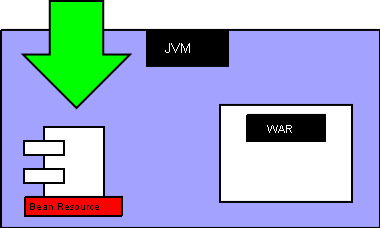

This Action configures a Tomcat Bean Factory Resource.
This resource factory can be used to create objects of any Java class that conforms to standard
JavaBeans naming conventions
Notice :
--------
This documentation contains excerpts from the Tomcat official site http://tomcat.apache.org, jndi-resources-howto.html
This documentation IS NOT the official documentation.
For the offical Tomcat doecumentation please refer to the previous Tomcat official site (http://tomcat.apache.org).
The resource factory will create a new instance for every lookup on it.
1. TOMCAT JNDI RESOURCES NAMESPACES
The following is a general rule for all for all the JNDI Resources configured inside Tomcat >= 5.
JNDI Resources can de declared at the global level or at the context level.
Tomcat 5 maintains a separate namespace of global resources for the entire server.
These are configured in the <GlobalNamingResources> element of $CATALINA_BASE/conf/server.xml.
You may expose these resources to web applications by using a <ResourceLink> to include it in the per-web-application context.
Converted into the Kikonf scheme the previous stanza means that the scope for a JNDI Resource is either :
_ Global using scope resources.global : true
or
_ Local using scope context (and/or an affiliated : context.global, default_context.global, default_context)
Note:
-----
When the Global Scope is requested for an Action setting resources.global to "true" into the Action file.
The use of context (and/or an affiliated : context.global, default_context.global, default_context) is allowed.
In this case the resource is declared at the Global level.
But a ResourceLink is also created for the provided context Scope.
This is the reason why, all the Kikonf Actions for Tomcat JNDI Resources alWays support a "link" tag.
2. USING BEAN FACTORY WITH TOMCAT
The following is a short tutorial about how to use a Bean Factory with Tomcat.
2.1. Create Your JavaBean Class
e.g.:
package com.mycompany;
public class MyBean {
private String foo = "Default Foo";
public String getFoo() {
return (this.foo);
}
public void setFoo(String foo) {
this.foo = foo;
}
private int bar = 0;
public int getBar() {
return (this.bar);
}
public void setBar(int bar) {
this.bar = bar;
}
}
2.2. Declare Your Resource Requirements
Add a resource-env-ref antry into your web application deployment descriptor web.xml:
<resource-env-ref>
<resource-env-ref-name>
bean/MyBeanFactory
</resource-env-ref-name>
<resource-env-ref-type>
com.mycompany.MyBean
</resource-env-ref-type>
</resource-env-ref>
2.3. Run Kikonf Action beanrsc
2.4. Sample code using the JavaBean Factory
Context initCtx = new InitialContext();
Context envCtx = (Context) initCtx.lookup("java:comp/env");
MyBean bean = (MyBean) envCtx.lookup("bean/MyBeanFactory");
writer.println("foo = " + bean.getFoo() + ", bar = " +
bean.getBar());

Trademarks :
- "Apache", "Apache Tomcat" and "Tomcat" are trademarks of the Apache Software Foundation.
- "Java" and "JVM" are a registred trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
- Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.